Cybersecurity leaders should be well-versed with current trends and best practices in security management to effectively manage the evolving threats and exposures they encounter every day without stifling their business ambitions.” – Gartner.
However, as cyber threats become increasingly elaborate, traditional measures to secure systems are usually inadequate. So how does one bolster an organization’s security?
Today, 70% of organizations are fighting a broad set of threats ranging from sophisticated malware to advanced persistent threats. The necessity of real time threat detection and response mechanisms has never been greater.
XDR, NDR, and EDR serve as strong detectors against this adversary. Let’s see why they are important.
Importance of NDR, EDR and XDR in Cybersecurity
With 80% of data breaches starting from compromised endpoints, it has now become crucial that EDR, NDR, and XDR should be included in your security strategy to protect sensitive information. Each one offers unique strengths that benefit an organization’s overall security posture in many ways. This includes the following:
1. Threat Detection and Response
2. Improve Incident Response
3. Reduce Risk
4. Improve Visibility
XDR vs NDR vs EDR: Pros and Cons
EDR, XDR, and NDR have different strengths that can be put to good use in a battle against new forms of cyber threats. Knowing the peculiar strengths and weaknesses of each will enable an organization to build a resilient security posture.
1. Pros and Cons of EDR
Pros
Focused on Endpoint Security: EDR has both a focus and specialty on the endpoint level of threat detection and response, offering very focused endpoint protection.
Behavioral Analysis: EDR conducts behavioral analysis so that in case of any anomalies, endpoint activities can be traced easily, which helps more in finding new and/or unknown threats than might be done by traditional signature-based approaches.
Quick Response: EDR solutions can trigger quick responses, such as isolating infected devices or killing malicious processes, and contain malware from spreading.
Integration Capabilities: EDR integrates well with other security tools, such as antivirus and SIEM systems, thereby giving a wider view of the attacks.
Cons
Scope Limitation: The prime focus of EDR is basically on the endpoints, and this might not allow them to show the attack which may be initiated through other vectors like networks or cloud environments.
FALSE Positives: The dependence upon behavioral analysis may result in false positives, leading to unnecessary alerts and enhancement in workload for security teams.
Reactive Approach: EDR’s prime reactions are toward post-threat scenarios, thus being less effective against high-order, persistent threats.
Skill Requirements: Managing an EDR solution requires skilled personnel in configurations, monitoring, and alert responses.
2. Pros and Cons of XDR
Pros
Comprehensive View: XDR offers a single source of truth for an organization about the posture of security across endpoints, networks, cloud, and identity layers, thereby offering an integrated approach to threat detection and response.
Correlation and Context Analysis: It makes use of deep correlation techniques that prioritize the threats, hence lessening false positives to allow focus on critical threats for security.
Automation and Orchestration: Adding automation and orchestration across various layers of security to improve the response efficiency of it-the speed of detection and response is, therefore, faster.
Wide Integration: XDR provides easy integration of a wide array of security and threat intelligence tools, ensuring that the overall security ecosystem is integrated.
Cons
Cost: The implementation and maintenance of XDR are very expensive, considering its integrated nature across diverse tools and the support it continues to demand.
Skill Requirements: Much like EDR, XDR requires expert staff to function its configuration, analyze alerts, and perform deep threat analysis.
Complexity: XDR has a broader scope and integration, which brings about its own configuration and management complexities, hard for thinly spread security resources organizations to manage.
Pros and Cons of NDR
Pros
Network-Centric Visibility: The prime focus of an NDR solution is the visibility within network traffic to detect threats that may evade endpoint security controls. Examples include the lateral movements inside the network.
Behavioral Analysis of Network Traffic: By analyzing pattern and behaviors inside the network, NDR can trace abnormal activities that may show a security breach.
Stealthy Threat Detection: NDR is great in threat detection, taking advantage of the network’s vulnerability. Examples are data exfiltration and anomalies in encrypted traffic.
Integration Capabilities: With NDR, there is an integration of other security platforms. This enhances their visibility and also provides them with contextual information in support of broader security strategies.
Cons
Limited Endpoint Visibility: Because NDR focuses on network traffic, it does not provide detailed insight into activities specific to the endpoint and, in some cases, may be blind to threats confined to just the endpoints themselves.
Complex Setup and Maintenance: NDR solutions are implemented in a very complex way in nature; this requires huge amounts of time and expertise for perfect configuration and maintenance.
FALSE Positives: Because it is dependent on behavioral analysis, just like EDR, NDR can generate false positives which may lead to unwanted alerts and extra workload for security teams.
Skill Requirements: Solutions of NDR require specialized knowledge related to network security, which can sometimes be a problem for an organization due to its limited in-house knowledge.
NDR vs EDR vs. XDR: Key Differences
1. Coverage
XDR (Extended Detection and Response):
The use of XDR in conjunction with endpoint devices, network traffic, cloud services, and email provides a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity. With this broad coverage, XDR can provide a complete security perspective, leading to faster and more precise threat detection and response across the organization’s entire IT infrastructure.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response):
Endpoint security is the primary objective of EDR. It also provides protection against the hacking of individual devices such as laptops, desktops and servers. Endpoint-level security is ensured through the provision of EDR solutions that offer endpoint specific threat detection, malware analysis, and incident response services.
NDR (Network Detection and Response):
The main focus of NDR is on network-level threats and anomalies. It tracks network traffic and device interactions to identify and respond to threats that may not be observable from the endpoint perspective. This focus assists in the detection and prevention of network-based attacks and suspicious activities.
2. Detection and Response Capabilities
XDR (Extended Detection and Response):
Identifies Complex threats, which connects data from endpoints to network traffic and cloud services for detection. The use of XDR can detect complex risks, including lateral movement or data exfiltration, through this comprehensive analysis. This technique is useful for these investigations. A broad range of response actions, such as network segmentation and cloud workload protection are available through XDR solution.
EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response):
Techniques such as endpoint-level EDR, signature-based detection (TOS), and behavioral analysis with machine learning algorithms are utilized to identify threats. All methods are supervised. EDR can respond to a potential threat by isolating the infected endpoint, disabling malicious software, or quarantining files.
NDR (Network Detection and Response):
The goal of NDR is to identify network-level threats by examining network traffic and device interactions.me. It also detects patterns and anomalies that indicate potential threats, such as lateral movement in the network. Among the capabilities of NDR is its response, which includes alerting and aiding in the mitigation or prevention of network-level threats.
Gain control over endpoints across Windows, Mac, and Linux systems. Key highlights include:
Automated Detection & Response
Rapid infected endpoint isolation
Reduced Alert Fatigue
3. Data Aggregation and Correlation
XDR:
It collects information from endpoint devices, network security tools, cloud services, identity solutions, and email security. It uses advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to analyze data and identify patterns and anomalies that could be a warning of danger.
EDR:
The primary source of endpoint-based data is end-point logs, events (e.g., event cancellation), and telemetry generated by end step security tools. It connects this data with the endpoint itself through a use of behavioral analysis and threat intelligence feeds to limit visibility into more general aspects of security, beyond just individual devices.
NDR:
It collects and analyses data gathered from network traffic and device interactions. It focuses on matching this data to identify network-level patterns and anomalies. NDR is a method of monitoring network communications to identify and respond to threats that impact the entire network.
4. Integration and Automation
XDR:
It works with all sorts of security tools across the entire stack, from mail protection to network access control and identity management to email intrusion prevention. XDR can be used in conjunction with SOAR solutions to provide automation capabilities that extend beyond the traditional security layers. The process involves automating intricate response workflows that involve multiple tools and teams, ultimately resulting in faster threat detection and response.
EDR:
Integrates with SIEM and other endpoint security tools. Isolation, process termination, and file quarantine are among the typical endpoint response actions that can be automated. XDR is not as widely integrated with network security tools.
NDR:
Can be integrated with network security devices and may also connect with SIEM systems to improve visibility. Automation is provided for network-based response actions and threat analysis. Conversely, its orchestration features tend to emphasize network-level responses and may not match the full range of XDR capabilities.
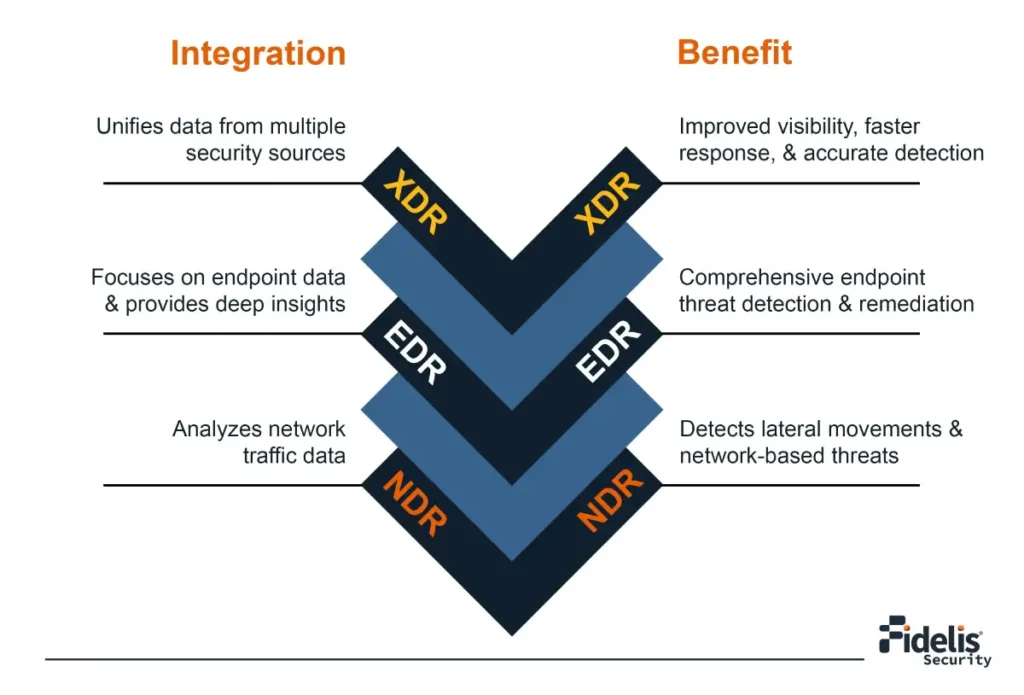
How Does the Integration of Data Differ Among XDR, EDR, and NDR Solutions?
Organizations employing integrated security platforms report 50% faster threat detection and response times than those using isolated solutions, according to IDC. This demonstrates how full visibility and efficient incident response across several security domains are facilitated by the combination of XDR, EDR, and NDR solutions.
Extended Detection and Response, or XDR
Endpoint Detection and Response, or EDR
Network Detection and Response, or NDR
In What Scenarios Would XDR Be More Beneficial Than EDR or NDR?
SolutionsScenariosBenefits
XDRXDR is best suited for organizations that need a holistic approach to security across diverse IT environments, integrating data from multiple sources for a unified view.XDR improves detection and response capabilities across endpoints, networks, and other security layers, making it ideal for complex infrastructures with varied security needs.EDREDR is most effective in environments heavily reliant on endpoints, where there is a need for in-depth visibility and control over endpoint-specific threats.EDR offers specialized detection and remediation techniques for endpoint threats, providing a focused approach to endpoint security.NDRNDR is beneficial for organizations that prioritize robust monitoring of network traffic to detect and respond to threats that occur within the network layer.NDR focuses on identifying network-based threats, such as lateral movement or data exfiltration, that might not be captured by endpoint-centric solutions
What Are the Main Challenges of Implementing XDR Compared to EDR/NDR?
XDR:
Challenges: Putting XDR into practice can be difficult since it involves managing and integrating several security products and data sources. This calls for coordination and a thorough strategy across several security domains. Resource Requirements: More resources are needed, such as trained staff to oversee the extensive integration and guarantee efficient threat identification and response.
EDR:
Challenges: Since EDR can only see endpoints, it cannot detect risks like network-based assaults that happen outside of endpoints. Moderate resource requirements with an emphasis on endpoint management and countering threats unique to each endpoint.
NDR:
Challenges: Because network encryption can mask malicious activity, NDR can have trouble identifying threats and does not provide endpoint visibility. Resource Requirements: Moderate, centered on the analysis and management of network traffic to identify and respond to threats.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between NDR, EDR and XDR
When consulting EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) versus XDR (Extended detection and response) and NDR (Network Detection Response) solutions, organizations must consider several issues, including, but not limited to, their security requirements and requirements, and budget resources, solution complexity, integration potential, false alarm rate, compliance, and regulatory needs, etc.
1. Security Outlay
2. Budget
The price option is a major factor since typically XDR solutions are costlier than both EDR and NDR due to a wider scope of integration to multiple systems and operations.
EDR is the most Economical for Endpoint Security Remedy in Case of Security Investments is NDR and XDR due to Broader Monitoring and Advanced Analytics. Organizations need to balance their budget with the level of security afforded by each of the solutions.
3. Resources
In addition to implementing these solutions, overseeing XDR and NDR systems may require extensive human resources who are able to set up and supervise the systems, respond to the incidents, and conduct detailed forensic investigations.
EDR may not be as resource hungry as XDR and NDR. Organizations must perform an assessment of their internal defense human resources and knowledge to ascertain whether they have the ability to deploy and sustain these solutions in a productive manner.
4. Complexities
Compared to EDR, NDR and XDR solutions which provide extensive integration and monitoring functions are more challenging to roll out and maintain. This presents a problem for organizations that do not have sufficient security technology and/or expert knowledge in the area of XDR and NDR as management of such solutions will be almost impossible hence EDR will be less challenging.
5. Integration Capabilities
One of the most appreciated capabilities of XDR is the synergy of different security solutions, which covers all components of the security belt of the organization and allows faster action against the threats. NDR, even though it is primarily about enhancing network visibility, gains context when integrated with other security solutions. Organizations need to take stock of the security systems available to determine whether they would be suited to the integrated approach of XDR or whether it is NDR only that needs to focus its attention to the networking components.
6. Compliance
Companies that operate in regulated sectors have to observe particular compliance standards that determine the type of security solutions they wish to use. The EDR, XDR, and NDR solutions all have scalable support for compliance with varying levels of confidence, being XDR with the highest level of confidence support because of being able to monitor more sources. Organizations should pay attention to their regulatory issues such that the chosen solution does contravene any statutory requirements.
Through due consideration of the mentioned factors, an organization is able to predetermine whether EDR, XDR or NDR will be suitable both for addressing the security concerns and internal operational conditions.
Which Threat Detection and Response Solution Is Best for Your Organization?
The endpoint level is where EDR effectively monitors, secures and mitigates issues, but it relies on the installation of an agent on every device that cannot function properly in cloud environments.
By utilizing an XDR approach, it becomes possible to provide more complete monitoring and data analysis across multiple streams on one platform. The majority of large companies will need to integrate EDR and NDR into their security plan to establish a robust and mature cybersecurity posture.
The final decision is based on your individual security requirements, existing infrastructure, and resources.
How Can Fidelis Security Help?
Connect with Fidelis Security for a more secure environment. EDR, NDR and XDP are integrated into our system for complete protection.’ Our platform integrates EDR, NDR, and XDR for comprehensive protection.
Key highlights include:
Unified, all-encompassing defense
cross-platform visibility
9x faster threat response
Our team provides you with top-notch threat intelligence, automation, and expert support to help you quickly identify and eliminate threats. We offer scalable solutions that are secure and compliant with SMBs and large enterprises. Requests for quotations are welcome. Trust Fidelis Security to safeguard your organization.?
The post Understanding XDR, NDR, and EDR: A Comprehensive Guide to Modern Cybersecurity Solutions appeared first on Fidelis Security.
No Responses